Did you know that patients that self-manage their healthcare at a high level are 9% more likely to have blood pressure within the normal range than those that don’t?
Studies show that patients who are more actively involved in their care will experience better long-term health outcomes and incur lower costs.
The key to integrated and successful patient engagement is having healthcare professionals provide patients with a treatment approach that is well-suited to their needs – but it can only be effective if patient activation is present within the treatment plan.
Read on to learn about patient engagement strategies to improve patient outcomes.

Public and private health care organizations are employing strategies to better engage patients, such as educating them about their conditions and involving them more in making decisions about their care.
Before diving into strategies on how to increase patient engagement, let us begin by explaining the definition of patient activation and how it differentiates from patient engagement.
What is Patient Activation and How Does It Increase Patient Engagement?
According to Judith Hibbard, Ph.D., MPH., patient activation can be defined as an individual’s knowledge, skill, and confidence in managing their own health and healthcare (Microsoft PowerPoint presentation, Can Increasing Patient Activation Improve the Outcomes of Care?, 2008).
In comparison, patient engagement is a broader concept that combines patient activation with interventions designed to increase activation and promote positive patient behaviour.
How can we measure patient activation?
Hibbard developed a patient activation measure (PAM), a validated survey that scores the degree to which someone sees themself as a manager of their health and care.
PAM is a validated questionnaire and survey consisting of 13 questions that segment individuals into 4 activation levels, along an empirically derived 100-point scale. The levels are the following:
- Level 1: Disengaged and Overwhelmed
- Level 2: Becoming Aware But Still Struggling
- Level 3: Taking Action and Gaining Control
- Level 4: Maintaining Behaviors and Pushing Further
The purpose of each level is to provide deeper insight into particular health-related characteristics that include an individual’s attitude, motivators, and behaviours.
Individuals who score in the lowest level of activation indicate that they don’t yet understand the importance of their role in managing their health and lack knowledge of health self-management skills.
Individuals in the highest activation level, on the other hand, are proactive with their health, have developed strong self-management skills, and are resilient in times of stress or change.
The 4 Levels of Patient Activation Explained
The four levels define the patient’s health literacy, which in return helps healthcare professionals provide the appropriate patient education and necessary resources to promote patient activation.
Key details about the 4 levels of patient activation:
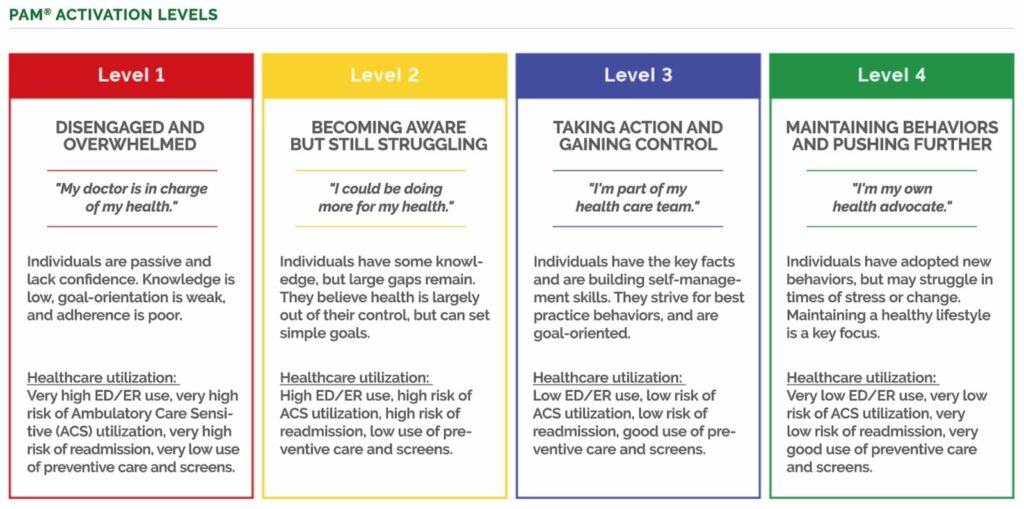
(Insignia Health, Patient Activation Measure® (PAM®) Survey Levels, 2019)
Clinicians will generally send the PAM questionnaire to their patients before the scheduled appointment time to gather insights, either through their patient portal or in the waiting room. The patient survey can be integrated with electronic medical records (EMR) so that the healthcare team is prepared ahead of time to better understand the patient’s level of activation.
The 4 Levels of Patient Activation Explained

1. Provide Patients with Adequate Education and Resources
Healthcare providers must do their due diligence to promote patient education if they’re looking to improve patient engagement rates.
This can be done by assessing patient health literacy (the capacity to seek, understand, and act on health information). One can assume that low health literacy can imply that the healthcare provider’s communication is poorly understood, leading to incomplete self-health management, responsibility, and insufficient health care optimization.
Promoting health literacy is the healthcare provider’s primary responsibility and how it’s done depends on a patient’s specific health interaction parameters. These can include the following:
- A patient’s physical setting
- Communication style
- Accessibility to resources
- Available time
- Modes of how the information is being provided.
Resources can include, but are not limited to the following:
- Brochures & printables
- Workshops
- Patient teach-back
- Written Instructions
- Verbal Instructions
- Infographics
- Online/website material
- Patient portal
- Access to appropriate healthcare providers
- Access to family and caregiver assistance
2. Patients Should Be Involved in Shared Decision-Making
It’s proven that when patients and providers work together to understand goals, outcomes, and patient engagement strategies, there’s an increase in patient satisfaction.
Patients are more likely to adhere to screening, diagnostic, or treatment plans and are known to have reduced decisional conflict and anxiety.
The clinician’s responsibility is to employ high-quality, reliable tools and skills for informed, shared decision-making amongst the patient and other caregivers.
3. Providing Support and Effective Communication Outside of the Office
In a 2015 research review of communication inefficiencies in healthcare, it was noted that poor communication has a number of adverse effects, including the following:
- A variety of negative outcomes
- Discontinuity of care
- Compromised patient safety
- Inefficient use of valuable resources
- Patient dissatisfaction
- Overworked physicians
- Negative economic consequences

It was noted that pre-assessments, process indicators, and follow-up tools were all resources that helped improve patient activation. The research review also indicated that face-to-face communication is recommended in practice, and that written communication remains the most common form of communication between healthcare professionals.
In the past, face-to-face appointments were not always easy to attend, but now, with technology advancements, face-face appointments can be conducted using video conferencing.
Innovations in care delivery are now focused on the patient-first approach. When it comes to self-management, there are tools that providers are using to help engage patients, such as:
- Patient reminders
- Patient portals
- SMS/Email communication
- Online booking
- Health apps & ePrescriptions
4. Leveraging Health Technology to Enhance Patient Engagement Strategies

More and more people are seeking health information online. In 2017, 72% of consumers found healthcare information on the internet, compared to only 60% in 2015 (Professional Research Consultants, Annual Report of Consumer Behavior, 2017).
Patients and families are utilizing communities, technology, and the internet to manage their care, gain support, and support others.
Along with increased technology usage, consumers have greater expectations for instant access to health services – which explains why the demand for health apps that increase patient engagement is on the rise, too.
Apps such as Fitbit and the Apple Health App give physicians the opportunity to sync these devices to electronic health records (EHR) to automatically download patient data and facilitate treatment outside of an office setting.
Interested in boosting patient engagement with practice management software?
Check out these blogs:
How To Increase Patient Engagement… And How Adracare Can Help

Patient engagement is not a “one size fits all” approach, but rather a tailored and meaningful approach that is specific to each individual’s level of patient activation & personal goals.
To increase patient engagement, providers and patients need to foster an authentic, timely, and mutually beneficial relationship with one another, as well as other organizations and third parties to better understand health knowledge gaps.
There are a variety of ways to increase patient engagement using the Adracare platform:
- Patients can access their medical records and test results, anywhere, from any device through an online portal
- Improve communication between providers, patients, caregivers, and third parties with secure email and texting
- Leverage a digital-first approach – patients can easily access video sessions without the need to download software
- Benefit from HD video conferencing with in-session chat, document sharing, and screen sharing
- Send automated appointment reminders
- Online booking & Scheduling
With Adracare’s all-in-one practice management and patient engagement solution, healthcare professionals are able to conveniently provide services to patients living in remote or rural areas, thus reducing the amount of missed appointments and encouraging patients to actively participate in their healthcare regime.
To learn more about how Adracare can help you and your clinic increase patient engagement and satisfaction, contact us today!





